If you’re considering a job that keeps you physically active and engaged in logistics, becoming a material handler might be the perfect career choice. Material handlers play a crucial role in ensuring smooth warehouse operations by moving, organizing, and managing goods. This article provides an in-depth look at the role, including job responsibilities, requirements, career prospects, and step-by-step guidance on how to enter this field.
What Does a Material Handler Do?
A material handler, also known as a warehouse associate, is responsible for moving products, merchandise, and materials within supply chains. They work across industries such as manufacturing, shipping, and retail. Their duties often include both physical and administrative tasks, ensuring the timely and accurate movement of goods.
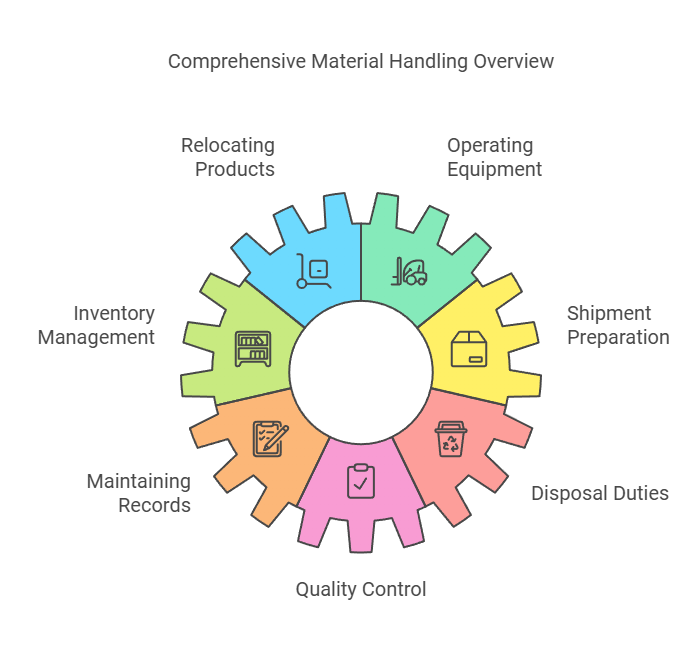
Key Responsibilities
- Relocating Products: Moving goods to and from storage areas, production floors, loading docks, and delivery trucks.
- Operating Equipment: Using forklifts, pallet jacks, and other tools to handle materials safely.
- Inventory Management: Recording inventory data using enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems or similar software.
- Shipment Preparation: Wrapping, securing, and staging goods for shipping.
- Maintaining Records: Keeping accurate documentation for all incoming and outgoing materials.
- Disposal Duties: Managing waste materials and ensuring proper disposal practices.
- Quality Control: Ensuring inspectors complete checks and coordinating repairs if necessary.
| Task | Details |
|---|---|
| Receiving Shipments | Inspect and process new shipments. |
| Inventory Documentation | Update ERP systems with inventory changes. |
| Equipment Operation | Use forklifts, manual jacks, and dollies to transport goods. |
| Shipment Preparation | Wrap and secure goods for transportation. |
| Problem Resolution | Address and resolve issues on production lines or during inventory checks. |
Salary and Job Outlook
Average Salary
Material handlers earn an average annual salary of $36,873. Salaries can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, and specific job responsibilities.
| Experience Level | Average Annual Salary |
| Entry-Level | $30,000 – $34,000 |
| Mid-Level | $35,000 – $42,000 |
| Senior-Level | $43,000+ |
Job Outlook
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, material handler jobs are expected to grow by 6% between 2021 and 2031. This growth reflects the increasing demand for logistics professionals in e-commerce, manufacturing, and other sectors.
Requirements for Material Handlers
Education
- Minimum: High school diploma or GED equivalent.
- Optional: Associate or bachelor’s degree in mathematics, business management, or logistics to enhance qualifications.
Training
- On-the-Job Training: Most entry-level roles provide training covering safety protocols, equipment operation, and organizational techniques.
- Specialized Training: Some employers provide specific training for handling hazardous materials or using advanced machinery.
| Training Type | Details |
| Safety Protocols | Learning OSHA standards and workplace safety practices. |
| Equipment Handling | Training on operating forklifts, pallet jacks, and computerized scales. |
| Inventory Management | Instruction on tracking and documenting stock accurately. |
Certifications
Earning certifications can improve job prospects:
- Forklift Operation Certification: Required by OSHA; renewed every three years.
- HAZMAT Certification: For handling hazardous materials; often involves self-guided courses and exams.
- Commercial Driver’s License (CDL): With hazardous material endorsement, if the job involves operating specific machinery.
| Certification | Requirement |
| Forklift Operation | Mandatory for forklift use; includes practical and theoretical components. |
| HAZMAT Certification | Essential for handling hazardous materials; periodic renewal required. |
| CDL with Endorsements | Required for certain heavy machinery roles, depending on the industry. |
Essential Skills for Material Handlers
| Skill | Importance |
| Communication | Effective verbal and written communication ensures smooth teamwork and accurate reporting. |
| Mathematics | Proficiency in basic math helps with inventory tracking and documentation. |
| Problem-Solving | Quick thinking and collaboration aid in resolving warehouse and logistics issues. |
| Organization | Maintaining an orderly workspace ensures efficiency and accuracy. |
| Physical Stamina and Strength | Necessary for lifting heavy materials and enduring long shifts in varying conditions. |
Work Environment
Material handlers typically work in warehouses or factories. The specific environment depends on the industry:
- Warehouse Operations: Moving consumer goods, maintaining inventory levels, and preparing shipments.
- Manufacturing Plants: Handling raw materials and ensuring production areas remain stocked.
- Specialized Environments: Managing hazardous materials or working in extreme temperatures.
| Factor | Description |
| Temperature | Work may involve hot, cold, or humid conditions. |
| Hours | Full-time roles often include rotating shifts; overtime common during peak periods. |
| Supervisory Structure | Material handlers report to warehouse managers or shift supervisors. |
Steps to Become a Material Handler
1. Earn a High School Diploma
- Focus on courses that enhance basic math, computer literacy, and communication skills.
2. Ensure Physical Fitness
- Build strength and stamina to handle the physical demands of the role, such as lifting heavy materials and standing for long hours.
3. Pursue Relevant Certifications
- Obtain certifications such as forklift operation or HAZMAT training to improve employability.
4. Develop Soft Skills
- Strengthen teamwork, communication, and organizational abilities to excel in a warehouse environment.
5. Create an Effective Resume
- Highlight relevant skills, certifications, and work or volunteer experience that demonstrate your qualifications.
| Step | Details |
| High School Diploma | Focus on basic skills necessary for logistics and warehouse roles. |
| Physical Fitness | Prepare for lifting, carrying, and long hours of physical work. |
| Certifications | Forklift operation, HAZMAT certification, or CDL endorsements. |
| Soft Skills | Emphasize communication, teamwork, and attention to detail. |
| Resume and Cover Letter | Tailor documents to showcase relevant experience and interest in the role. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Material Handlers
1. What are the duties of a material handler?
The duties of a material handler encompass a wide range of responsibilities essential for efficient warehouse operations. Primarily, material handlers are tasked with moving, storing, and organizing goods within supply chains. They load and unload items from delivery trucks, transport materials to storage or production areas, and ensure goods are staged correctly for shipment. Other responsibilities include maintaining inventory records, using tools such as forklifts or pallet jacks, and adhering to safety protocols. Material handlers may also be involved in quality checks, waste management, and assisting inspectors to address any issues. These duties require physical stamina, organization, and communication skills to ensure warehouse operations remain productive and accurate.
2. What is the highest pay for a material handler?
The highest pay for a material handler can vary based on factors such as location, industry, and experience level. Senior-level material handlers or those working in specialized industries, such as hazardous material handling, can earn upwards of $50,000 to $60,000 annually. Additional certifications, such as forklift operation or HAZMAT endorsement, and experience with advanced inventory systems can also boost earning potential. Geographic location plays a role as well, with material handlers in metropolitan areas or regions with high-demand industries typically earning higher wages. For example, a material handler in a tech manufacturing hub may earn more than one in a rural logistics center.
3. What is the work of material handling?
Material handling involves the movement, protection, storage, and control of goods throughout supply chains. This work ensures that materials flow efficiently from suppliers to production areas and eventually to customers. Material handling includes both manual and automated processes, such as operating machinery to lift heavy items, recording inventory changes, and ensuring goods are safely packaged for transportation. The goal is to maintain an organized and efficient workflow that reduces costs, minimizes errors, and ensures timely deliveries.
4. Is a material handler the same as a warehouse worker?
While the roles of a material handler and warehouse worker overlap, they are not identical. Material handlers specifically focus on the movement and management of materials, often using specialized equipment like forklifts. Warehouse workers may have a broader range of responsibilities, including stocking shelves, cleaning the workspace, and fulfilling customer orders. Material handlers typically operate more in logistics and inventory management, whereas warehouse workers may engage more in order processing and general warehouse upkeep.
5. Is a material handler the same as a forklift operator?
A material handler and a forklift operator are related but distinct roles. Forklift operators specialize in using forklifts to move heavy materials, often as a primary job function. Material handlers may operate forklifts but also perform additional tasks, such as inventory tracking, packing goods, and coordinating shipments. While forklift operation is a skill within the material handler’s role, it is not the sole responsibility, making the material handler’s position more versatile.
6. What is the difference between a material handler and a package handler?
The difference between a material handler and a package handler lies in the scope of their work. Material handlers manage a variety of goods, including raw materials, production items, and consumer products, throughout supply chains. Package handlers, on the other hand, focus primarily on handling packages for delivery services, such as sorting, labeling, and loading parcels onto delivery vehicles. Material handlers often require more diverse skills and certifications, while package handlers’ tasks are typically more repetitive and focused.
7. Are material handlers direct labor?
Material handlers are often considered part of direct labor, especially in manufacturing and production settings. They contribute directly to the handling and movement of materials that are essential to the production process. By ensuring raw materials are available and finished goods are transported efficiently, material handlers support the core operations of a business. However, their classification can vary depending on the specific industry and organizational structure.