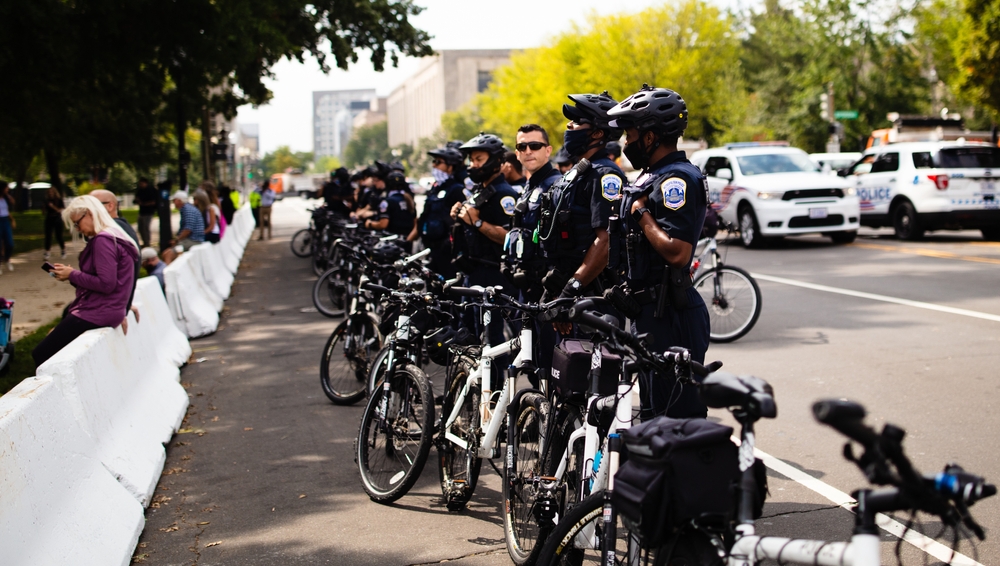
Corporate Strike Security: A Comprehensive Guide
I. Understanding the Modern Landscape of Labor Strikes from “Corporate Strike Security – Navigating Modern Challenges” by RSS Inc.
This section explores the evolving nature of labor strikes, moving beyond traditional picketing to encompass more complex and multifaceted disputes. It delves into the impact of technological advancements, globalization, the regulatory environment, and economic pressures on contemporary labor strikes.
II. Key Components of Corporate Strike Security
This section outlines the crucial elements of a comprehensive corporate strike security strategy. It emphasizes the importance of risk assessment and planning, employee relations and communication, physical security measures, legal and compliance considerations, and crisis management and communication.
A. Risk Assessment and Planning
- This subsection focuses on identifying potential vulnerabilities in operations, facilities, and supply chains, analyzing the likelihood of strikes, and developing detailed contingency plans for various scenarios.
B. Employee Relations and Communication
- This subsection stresses the importance of fostering positive employee relationships, maintaining open communication during disputes, and providing clear information to manage perceptions and reduce tensions.
C. Physical Security Measures
- This subsection addresses the implementation of physical security measures to protect company property, assets, and personnel, including access control systems, surveillance, security personnel, and transportation arrangements.
D. Legal and Compliance Considerations
- This subsection highlights the importance of understanding relevant labor laws and regulations, staying informed about legal challenges, and working closely with legal counsel to ensure compliance and develop strategies.
E. Crisis Management and Communication
- This subsection focuses on establishing a crisis response team, developing a media relations strategy, and designating a spokesperson for consistent messaging during strikes.
III. Best Practices for Mitigating Risks
This section provides practical advice on minimizing the risks associated with labor strikes. It advocates for proactive engagement with labor unions and employees, regular training and preparedness exercises, leveraging technology for risk management and monitoring, and collaboration with security experts and law enforcement.
A. Proactive Engagement
- This subsection emphasizes the importance of proactive dialogue with labor unions and employee representatives, addressing concerns before they escalate, and regularly reviewing and updating employee policies and benefits.
B. Training and Preparedness
- This subsection highlights the necessity of conducting regular training sessions on strike security protocols and procedures and simulating strike scenarios to test contingency plans and identify areas for improvement.
C. Technology Integration
- This subsection advocates utilizing technology to monitor and manage strike-related risks, using data analytics to predict labor unrest, and deploying security technologies to safeguard assets and monitor social media discussions.
D. Collaboration with Security Experts
- This subsection recommends partnering with security experts and consultants to develop robust strike security strategies and engaging with local law enforcement agencies for coordination and support during strikes.
IV. Impact of Labor Strikes on Business Operations
This section analyzes the far-reaching consequences of labor strikes on business operations, including both direct and indirect costs. It examines the impact on production schedules, customer satisfaction, revenue, operational expenses, reputation, and public perception.
A. Direct Costs
- This subsection details the immediate financial losses due to production halts, delays in fulfilling orders, contractual penalties, and the increased costs of hiring temporary workers or paying overtime to maintain operations.
B. Indirect Costs
- This subsection explores the long-term consequences of strikes, such as damaged customer relationships, reduced customer loyalty, negative public perception, and the need for public relations campaigns to rebuild the company’s image.
V. Role of Leadership in Managing Strikes
This section underscores the crucial role of effective leadership in navigating labor strikes. It emphasizes the need for leaders to balance business needs with employee concerns, demonstrate empathy, and maintain operational integrity.
A. Key Leadership Qualities
- This subsection highlights the essential leadership qualities of clear and consistent communication during strikes, providing regular updates to all stakeholders, and demonstrating understanding and fairness to de-escalate tensions and work towards resolutions.
B. Strategic Decision-Making
- This subsection focuses on the importance of identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies, including financial planning, ensuring alternative resources, and engaging in effective negotiation with labor unions and employee representatives.
VI. Legal Implications of Labor Strikes
This section provides an overview of the legal aspects of labor strikes, emphasizing the importance of understanding employee rights, employer obligations, and compliance with relevant regulations.
A. Key Legal Considerations
- This subsection explains the legal right to strike in many jurisdictions, outlining the scope and conditions under which it applies, and the importance of adhering to collective bargaining agreements outlining dispute resolution mechanisms.
B. Legal Strategies
- This subsection emphasizes the need for companies to work closely with legal counsel to ensure compliance, develop legal strategies for managing strikes, and meticulously document all communications, negotiations, and actions taken during a strike.
VII. Technology’s Role in Modern Strike Management
This section explores the various ways technology can be leveraged to effectively manage labor strikes, encompassing communication, security, and operational continuity.
A. Communication Platforms
- This subsection describes the use of platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams for real-time communication among management and non-striking employees and the utilization of social media and corporate websites for public and stakeholder communication.
B. Security Technologies
- This subsection discusses the application of modern surveillance technologies like CCTV and drone monitoring to enhance facility security during strikes, as well as the use of advanced access control systems to prevent unauthorized entry and ensure personnel and property safety.
C. Operational Technologies
- This subsection explores how technology can be used to monitor and manage supply chain disruptions caused by strikes, ensuring minimal impact on production, and how data analytics can help predict potential strikes and develop preemptive strategies.
VIII. Psychological Impact of Strikes on Employees
This section delves into the psychological effects of strikes on both striking and non-striking employees, examining the emotional and mental health consequences and offering guidance on providing support and maintaining morale.
A. Striking Employees
- This subsection discusses the financial and emotional stress experienced by striking employees due to loss of income and job security concerns, as well as the potential for both solidarity and internal conflicts within the workforce.
B. Non-Striking Employees
- This subsection examines the increased workload and pressure experienced by non-striking employees, their potential for burnout and decreased morale, and the possible conflicts they face between loyalty to the company and empathy for striking colleagues.
IX. Financial Preparedness for Strikes
This section highlights the critical importance of financial preparedness in mitigating the disruptive effects of strikes, including lost revenue, increased operational costs, and potential legal expenses.
A. Building Financial Resilience
- This subsection focuses on establishing reserve funds for crisis management, evaluating insurance policies for business interruption coverage, and implementing cost management strategies to maintain financial stability.
B. Financial Impact Analysis
- This subsection emphasizes the importance of conducting financial impact analyses for various strike scenarios, understanding potential costs, and developing appropriate response strategies, including scenario planning for short-term and prolonged strikes and revenue diversification.
C. Financial Communication
- This subsection stresses the need for clear and transparent communication with investors about the financial implications of strikes and the steps taken to mitigate them, as well as internal communication to align management and employees on the company’s approach.
X. Psychological Support and Employee Well-Being
This section focuses on the importance of addressing the psychological impact of strikes on employees and providing support to maintain morale and productivity.
A. Psychological Support Programs
- This subsection outlines the use of Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) to provide counseling and support services and the provision of mental health resources like workshops, webinars, and informational materials on stress management and resilience building.
B. Creating a Supportive Work Environment
- This subsection emphasizes the importance of fostering open communication, encouraging support networks, and promoting work-life balance through flexible work arrangements and wellness programs.
C. Training and Development
- This subsection discusses the value of providing resilience training to equip employees with stress management and adaptability skills and offering conflict resolution training to address disputes constructively.
XI. Final Thoughts on Corporate Strike Security
This concluding section reiterates the importance of a proactive and comprehensive approach to corporate strike security, emphasizing the need for preparedness, adaptability, and a commitment to maintaining business continuity and safeguarding corporate assets during labor disputes.