What staff augmentation solutions actually mean in practice
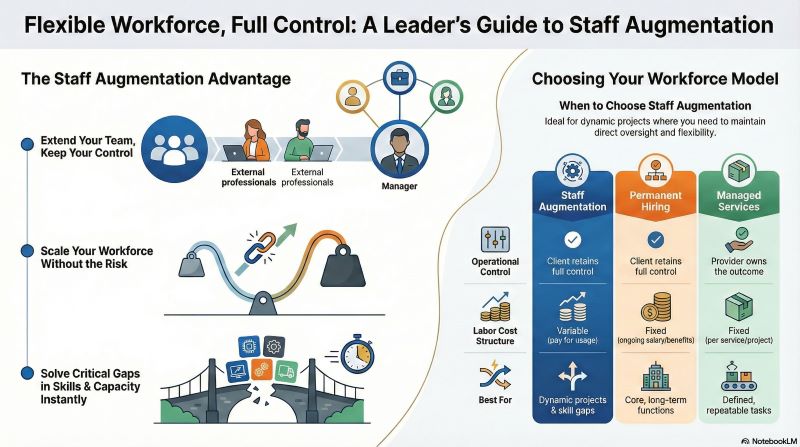
Staff augmentation solutions are a workforce model that allows organizations to extend internal teams with external professionals who operate within existing structures and management. Unlike outsourcing, augmented staff integrate directly into daily workflows, reporting lines, and operational systems while remaining employed by a staffing provider. This approach preserves internal control while expanding capacity or expertise.
The defining feature of staff augmentation is operational continuity. Teams retain ownership of priorities, processes, and outcomes while supplementing labor where gaps exist. This makes the model particularly effective for organizations that already have functional leadership and infrastructure but lack sufficient personnel to execute at required speed or scale.
Why organizations rely on staff augmentation instead of permanent hiring
Organizations rely on staff augmentation when permanent hiring introduces structural friction that slows execution or increases risk. Fixed headcount models are often poorly suited to environments where demand, scope, or skill requirements change faster than hiring cycles can adapt.
Common drivers behind this reliance include:
- Long hiring timelines that delay project start dates or operational recovery
- Fixed overhead costs tied to benefits, payroll, and long-term employment obligations
- Inflexibility in headcount that creates inefficiency during demand fluctuations
- Misalignment with project-based or cyclical workloads where needs are temporary by design
Staff augmentation allows organizations to adjust workforce levels without triggering internal restructuring or long-term financial commitments.
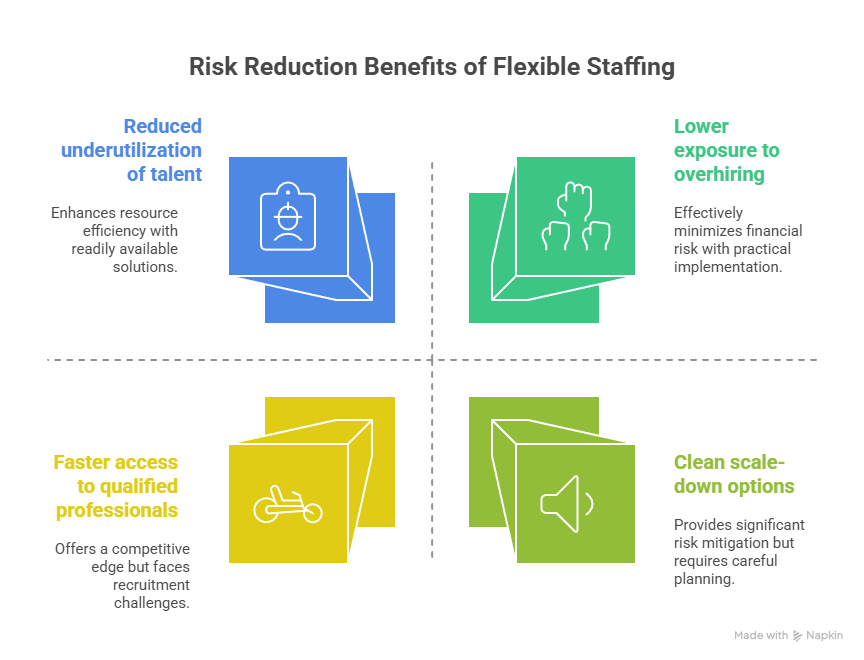
The model also reduces exposure to hiring risk by narrowing engagement to clearly defined scopes and timeframes. Instead of committing to permanent roles before demand stabilizes, organizations deploy skills only when and where they are required.
Risk reduction benefits include:
- Lower exposure to overhiring when demand softens or projects conclude
- Reduced underutilization of specialized talent outside active work periods
- Faster access to qualified professionals without prolonged recruitment cycles
- Clean scale-down options that preserve operational stability as needs change
This combination of flexibility, control, and risk containment explains why staff augmentation continues to replace permanent hiring in execution-driven environments.
Operational differences between staff augmentation and traditional staffing
Traditional staffing focuses on filling open roles, often with limited integration beyond task execution. Staff augmentation prioritizes embedded contribution, with workers functioning as true extensions of internal teams rather than temporary substitutes. This distinction affects productivity, accountability, and knowledge transfer.
Augmented professionals are expected to adapt to internal systems, tools, and performance standards. The staffing partner supports compliance, payroll, and workforce logistics, but day-to-day execution remains under the client’s direction. This separation of operational control from employment administration is central to the model’s effectiveness.
Staff augmentation versus managed services in real-world use
Staff augmentation places responsibility for delivery with the client, while managed services transfer outcome ownership to an external provider. In augmentation, internal leaders define priorities, oversee performance, and manage deliverables directly. Managed services, by contrast, bundle labor with process ownership and service-level commitments.
Organizations choose augmentation when they want flexibility without relinquishing control. Managed services are better suited to fully defined, repeatable functions, whereas augmentation excels in dynamic environments where priorities evolve and internal oversight is essential.
Common workforce challenges staff augmentation is designed to solve
Staff augmentation addresses capacity constraints, skill shortages, and timing mismatches that slow execution. Many organizations face periods where demand spikes faster than hiring pipelines can respond. Augmentation fills that gap without disrupting long-term workforce planning.
The model also resolves specialization issues. When expertise is needed in areas such as engineering, logistics, manufacturing support, or technical operations, augmentation provides targeted skills without requiring internal retraining or permanent role creation.
Types of roles most frequently filled through staff augmentation
Staff augmentation is most effective for roles with clearly defined responsibilities and measurable output. Technical, operational, and project-based positions are common because performance can be assessed within existing frameworks. These roles benefit from immediate contribution rather than extended onboarding.
In industrial and operational environments, augmentation often supports production, maintenance, quality control, and logistics functions. In professional settings, it frequently covers IT, engineering, analytics, and project management. The unifying factor is the need for speed and precision.
How staff augmentation supports scalability without operational disruption
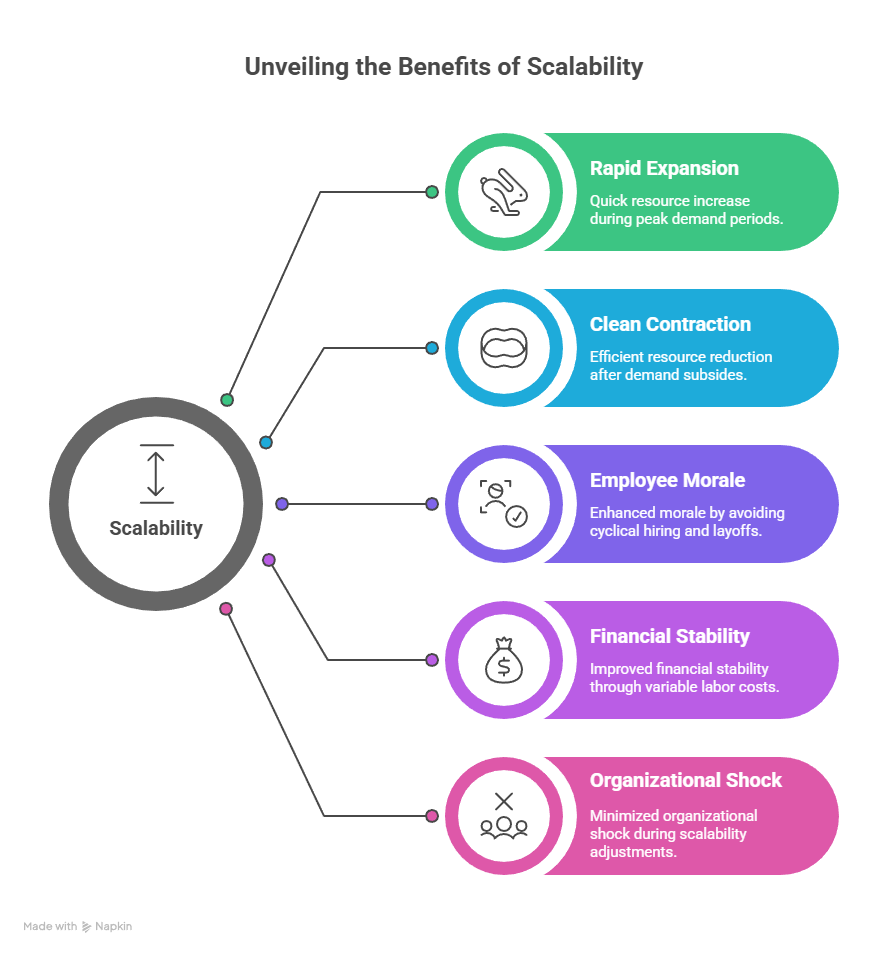
Staff augmentation supports scalability by aligning workforce capacity with real-time demand rather than long-range forecasts. Organizations expand and contract teams in response to actual workload, avoiding the structural strain created by permanent headcount changes.
Key scalability advantages include:
- Rapid expansion during peak demand without delaying execution
- Clean contraction after demand subsides without layoffs or workforce instability
- Protection of employee morale by avoiding cyclical hiring and reductions
- Improved financial stability through variable labor costs tied to active work
This responsiveness allows organizations to scale deliberately without introducing organizational shock.
Operational continuity is preserved because augmented staff integrate directly into existing teams and systems. Scaling occurs within established structures rather than requiring process redesign or management reconfiguration.
Continuity benefits include:
- No disruption to reporting lines or decision authority
- Consistent workflows and performance expectations during scale changes
- Minimal onboarding friction due to alignment with current processes
- Sustained execution speed throughout growth or contraction cycles
By scaling within existing frameworks, staff augmentation enables flexibility without sacrificing operational control or consistency.
The role of onboarding and integration in successful augmentation
Effective staff augmentation depends on structured onboarding that mirrors internal standards. Augmented professionals must understand workflows, safety requirements, communication norms, and performance expectations from the outset. Poor integration undermines the value of the model.
Strong staffing partners support this process by pre-screening candidates for adaptability and readiness. When onboarding aligns with internal practices, augmented staff reach productivity quickly and contribute with minimal supervision overhead.
Managing augmented staff without increasing internal complexity
Augmented staff are managed like internal employees in terms of daily direction, but administrative burdens remain with the staffing provider. This separation reduces HR workload while preserving operational authority. Managers focus on execution rather than employment logistics.
Clear role definitions, reporting lines, and performance metrics prevent confusion. When expectations are explicit, augmented staff operate with autonomy while remaining aligned with organizational goals.
Cost structure considerations in staff augmentation models
Staff augmentation operates on a variable cost structure that aligns labor spending with active demand. Organizations incur costs only when work is being performed, avoiding fixed employment expenses that persist regardless of workload. This model is especially effective for project-based, seasonal, or fluctuating operational needs.
The distinction becomes clearer when staff augmentation is compared directly to permanent hiring.
| Cost Dimension | Staff Augmentation | Permanent Hiring |
| Labor cost type | Variable, usage-based | Fixed, ongoing |
| Payment duration | Only during active engagement | Continuous, regardless of workload |
| Benefits and payroll overhead | Managed by provider | Fully absorbed by employer |
| Recruiting and hiring costs | Typically embedded in service | Separate and recurring |
| Idle labor risk | Minimal | High during demand slowdowns |
| Workforce adjustment | Scales up or down cleanly | Requires restructuring or layoffs |
| Budget predictability | High for defined scopes | Lower when demand fluctuates |
While hourly or contract rates in staff augmentation can appear higher than internal wages when viewed in isolation, direct rate comparisons rarely reflect total employment cost. Permanent hiring introduces additional expenses tied to benefits administration, recruiting cycles, onboarding time, and periods of underutilization.
From a financial perspective, staff augmentation delivers value through:
- Cost alignment with actual workload, rather than forecasted demand
- Reduced exposure to idle capacity during slow periods
- Faster deployment, which limits revenue loss or project delay costs
- Simplified budgeting for time-bound or variable initiatives
The economic advantage of staff augmentation lies in flexibility, speed, and risk containment, not in competing on base labor rates alone.
Compliance and risk management within staff augmentation solutions
Staff augmentation shifts many employment-related risks to the provider. Payroll administration, benefits, tax compliance, and employment regulations are handled externally, reducing exposure for the client organization. This is particularly valuable in multi-state or regulated environments.
However, operational compliance remains a shared responsibility. Clients must ensure augmented staff follow internal policies, safety standards, and regulatory requirements. Effective coordination between provider and client mitigates risk on both sides.
Measuring effectiveness of staff augmentation engagements
Effectiveness is measured through productivity, speed to contribution, and alignment with internal objectives. Augmented staff should deliver comparable output to internal employees within a short timeframe. Prolonged ramp-up indicates integration or selection issues.
Retention over the project lifecycle is another indicator. High turnover among augmented staff often signals misalignment between role expectations and candidate capabilities. Strong providers prioritize fit to maintain continuity.
When staff augmentation is not the right solution
Staff augmentation is less effective when organizations lack internal leadership or clear direction. Without defined priorities and management capacity, augmented staff may struggle to deliver value. In such cases, managed services or outsourcing may be more appropriate.
The model is also unsuitable for highly confidential or strategic roles that require long-term institutional knowledge. Augmentation excels in execution-focused contexts rather than foundational leadership positions.
Industry contexts where staff augmentation delivers the most value
Industries with variable demand and technical complexity benefit most from staff augmentation. Manufacturing, logistics, warehousing, and industrial services often face fluctuating labor needs tied to contracts or production cycles. Augmentation aligns workforce levels with operational reality.
Professional services and technology-driven sectors also leverage augmentation to access specialized skills quickly. The model supports innovation and responsiveness without locking organizations into fixed staffing structures.
Why Regional Supplemental Services (RSS Inc.) sets the standard for staff augmentation
Regional Supplemental Services (RSS Inc.) sets the standard for staff augmentation by operating at the intersection of workforce discipline and operational reality. Rather than positioning augmentation as interchangeable labor, RSS Inc. treats every engagement as an extension of the client’s operating model. This approach prioritizes execution consistency over volume-based placement.
RSS Inc. brings deep familiarity with industrial, technical, and operational environments where staffing precision directly affects output, safety, and reliability. Augmented personnel are selected based on their ability to function inside established workflows, not just their availability. This reduces ramp-up time and preserves internal performance standards.
Operational alignment over generic staffing
RSS Inc. differentiates itself through an operational-first staffing philosophy. Workforce decisions are informed by how roles actually function on the floor, in the field, or within production environments. This alignment minimizes the gap between expected and actual performance.
Key alignment factors include:
- Clear understanding of role-specific responsibilities and constraints
- Matching candidates to existing processes, tools, and supervision models
- Staffing designed to support productivity without altering internal structure
This ensures augmented staff integrate cleanly rather than forcing organizations to adapt around them.
Candidate readiness as a baseline requirement
RSS Inc. emphasizes readiness as a non-negotiable standard. Augmented professionals are expected to contribute immediately within established systems, reducing the need for prolonged orientation or corrective oversight. This focus protects internal managers from unnecessary supervision burden.
Readiness is reinforced through:
- Role-specific screening aligned to real operational conditions
- Verification of experience relevant to the actual work environment
- Expectation of accountability equivalent to internal personnel
As a result, productivity is stabilized early in the engagement.
Accountability that preserves client control
RSS Inc. maintains a clear separation between workforce administration and operational authority. Employment logistics, compliance, and workforce continuity are handled externally, while clients retain full control over priorities, scheduling, and performance direction. This structure reinforces accountability without diluting leadership control.
The model supports:
- Direct day-to-day management by internal supervisors
- Transparent performance expectations and escalation paths
- Workforce adjustments without operational disruption
This balance allows organizations to scale confidently without compromising governance.
Safety and consistency in execution-focused environments
In environments where safety, compliance, and repeatability matter, inconsistency introduces risk. RSS Inc. embeds safety awareness and execution discipline into its staffing approach, ensuring augmented teams operate within defined standards from the outset. This reduces operational variance across shifts or project phases.
Consistency is maintained through:
- Alignment with site-specific safety and compliance expectations
- Staffing continuity that minimizes turnover during active engagements
- Reinforcement of standard operating procedures rather than workarounds
This stability supports predictable outcomes in high-dependence roles.
How provider selection influences augmentation outcomes
The quality of a staff augmentation engagement is determined largely by the provider’s screening and matching process. Providers that emphasize volume over fit introduce risk and inefficiency. Effective partners prioritize role clarity, skill verification, and cultural alignment.
Long-term success also depends on responsiveness. Providers must adjust quickly when requirements shift or issues arise. This agility differentiates strategic partners from transactional vendors.
Integrating staff augmentation into long-term workforce strategy
Staff augmentation should complement, not replace, internal workforce planning. Organizations that integrate augmentation into strategic forecasts gain flexibility without eroding institutional knowledge. Internal teams remain the core, while augmentation absorbs variability.
Over time, data from augmentation engagements can inform hiring decisions. Patterns in demand and performance help leaders identify which roles warrant permanent investment and which are better served through flexible staffing.
Maintaining knowledge continuity with augmented teams
Knowledge continuity is preserved through documentation, collaboration, and overlap with internal staff. Augmented professionals should contribute to shared systems rather than operating in isolation. This approach ensures insights and progress remain accessible after assignments conclude.
Structured handoffs at project completion further protect continuity. When knowledge transfer is planned, organizations retain value beyond the duration of the engagement.
Decision criteria for adopting staff augmentation solutions
Organizations should assess internal management capacity, workload volatility, and skill gaps before adopting staff augmentation. The model performs best when objectives are defined and oversight is available. Clarity enables rapid deployment and consistent results.
Budget flexibility and risk tolerance also factor into the decision. Staff augmentation favors organizations that value adaptability and control over long-term staffing commitments.
FAQs
What are staff augmentation solutions?
Staff augmentation solutions allow organizations to add external professionals to internal teams on a temporary or flexible basis while maintaining direct operational control.
How is staff augmentation different from outsourcing?
Staff augmentation integrates external workers into internal workflows under client management, while outsourcing transfers responsibility for outcomes to an external provider.
Which roles are best suited for staff augmentation?
Roles with defined responsibilities and measurable output, such as technical, operational, and project-based positions, are best suited for staff augmentation.
Is staff augmentation cost-effective compared to hiring?
Staff augmentation can be cost-effective by reducing recruiting time, benefits overhead, and idle capacity, especially for short-term or variable needs.
How long do staff augmentation engagements typically last?
Engagements vary from weeks to months depending on project scope, workload volatility, and organizational needs.
How do organizations manage augmented staff day to day?
Augmented staff are managed like internal employees for daily tasks and performance, while administrative responsibilities remain with the staffing provider.
What should companies look for in a staff augmentation provider?
Key factors include candidate quality, responsiveness, industry experience, and the ability to align staffing with operational realities.