In today’s fast-paced, unpredictable business landscape, organizations face a growing number of disruptions—from labor strikes and talent shortages to geopolitical conflict and global pandemics. The nature of these disruptions has shifted, demanding a more proactive and comprehensive approach to risk management. In the face of these challenges, contingency planning has emerged as a mission-critical element of workforce management, moving beyond a theoretical exercise to a practical necessity for sustained success.
While traditionally associated with IT for disaster recovery, finance for economic downturns, or operations for supply chain interruptions, contingency planning from a staffing perspective is now essential for businesses aiming to maintain operational continuity and competitive agility. This involves anticipating potential workforce disruptions and developing strategic responses to mitigate their impact. It’s about building a robust and adaptable workforce that can navigate unforeseen challenges, ensuring that critical functions remain staffed and productivity is maintained, even when the unexpected occurs. This shift in focus acknowledges that an organization’s most valuable asset is its people, and their availability and capability are fundamental to resilience.
What Is Contingency Planning in Staffing?
Contingency planning in staffing refers to the proactive development of strategies, protocols, and resources to ensure a business can maintain essential workforce operations in the event of unexpected personnel disruptions. These disruptions may be caused by:
- Labor strikes
- Sudden resignations or leadership exits
- Health emergencies (e.g., COVID-19)
- Regulatory shutdowns
- Seasonal surges in demand
- Geopolitical issues
- Talent shortages in key roles
- Technological or system failures impacting HR processes
Rather than reacting to a crisis in the moment, staffing contingency planning prepares businesses to pivot with minimal interruption to productivity.
Why Staffing Contingency Planning Matters More Than Ever
1. Labor Market Volatility
The post-pandemic job market has revealed just how fragile staffing pipelines can be. Record quit rates, evolving work expectations, and a shortage of skilled labor in sectors like nursing, logistics, and IT have made staffing a moving target.
2. Operational Continuity
Downtime caused by staffing disruptions can be costly. In manufacturing, even a day of halted production due to insufficient labor can translate into millions in losses. In healthcare, understaffing can directly impact patient care.
3. Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Certain industries (e.g., food processing, transportation, public services) must meet strict regulatory standards. Staffing gaps that cause non-compliance can lead to hefty fines or legal ramifications.
4. Brand and Reputation Management
An unprepared organization that fails to fulfill commitments due to staffing failures risks its credibility. Clients, partners, and the public notice when a company stumbles.
Elements of a Staffing Contingency Plan
A comprehensive staffing contingency plan should include:
1. Risk Assessment
Identify vulnerable staffing areas based on role criticality, employee turnover rates, and external threats. Ask:
- What positions are mission-critical?
- Which departments are understaffed?
- Are there single points of failure?
2. Scenario Planning
Forecast potential disruption scenarios. Examples:
- A labor union initiates a strike.
- A competitor poaches a cluster of key employees.
- A natural disaster renders a regional office inoperable.
- A pandemic creates high absenteeism across departments.
Each scenario should include projected impacts and fallback staffing solutions.
3. Resource Mapping
Maintain a living database of:
- Internal talent pools (cross-trained or high-potential staff)
- External staffing partners and temp agencies
- Remote and gig workers ready for rapid deployment
- Retired or inactive staff who can be reactivated
4. Cross-Training Programs
Cross-training employees is one of the most effective internal risk mitigators. Employees capable of taking on multiple roles can help plug gaps quickly during a disruption.
5. Temporary Staffing Contracts
Pre-negotiated relationships with staffing agencies—especially those specializing in rapid deployment—should be a central pillar of your plan.
6. Digital Workforce Tools
Utilize workforce management software to track employee availability, location, and skills in real time. Advanced systems can suggest redeployments or schedule changes when staffing gaps occur.
7. Communication Framework
A disruption-response communication protocol should include:
- Designated point people per department
- Pre-written internal and external communications
- Contact lists for alternate staffing providers
- Message templates for employee notifications
8. Review and Update Cycle
Plans should be revisited quarterly or following any major workforce event. A static plan is as dangerous as no plan at all.
Building Your Staffing Contingency Strategy: Step-by-Step
Here’s how to create and implement a staffing contingency plan from the ground up:
Step 1: Form a Workforce Continuity Task Force
Include leaders from HR, operations, finance, legal, and communications. This cross-functional team will oversee risk identification, policy creation, and response coordination.
Step 2: Conduct a Staffing Vulnerability Audit
Analyze workforce data to identify where disruptions are most likely. Use tools like heat maps or risk matrices to visualize exposure.
Step 3: Draft Role-Specific Contingency Plans
For each high-priority role or department, outline:
- The expected impact of absence
- Backup personnel
- Expected time to fill via external partner
- Work-from-home contingencies (if applicable)
- Productivity benchmarks to maintain during disruption
Step 4: Establish Bench Talent and Partnerships
Create relationships with:
- On-demand staffing agencies
- Fractional workers or contractors
- Retired alumni networks
- Online freelancer platforms (for knowledge workers)
Having talent sources pre-vetted and under contract minimizes downtime.
Step 5: Train for Flexibility
Create cross-training pathways and shadowing programs. Encourage multi-role adaptability, especially for operational roles.
Step 6: Stress-Test the Plan
Run simulations quarterly. Include role-play disruptions and see how quickly departments can pivot. Assess communication speed, redeployment time, and business impact.
Step 7: Build Plan into Culture and Onboarding
Ensure managers and employees know where to access contingency materials. Make it part of the onboarding process for new HR team members.
Use Cases of Staffing Contingency Planning by Industry
Healthcare
During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals without contingency staffing strategies were forced to delay surgeries or shut down entire units. Those with pre-established relationships with travel nurse agencies and float pools were able to maintain services under pressure.
Logistics and Warehousing
Global supply chains are highly sensitive to labor disruptions. Companies like FedEx and Amazon utilize seasonal hiring ramps, but also build surge capacity into contracts with warehouse staffing vendors to ensure timely fulfillment even during black swan events.
Manufacturing
When skilled machinists go on strike or leave suddenly, entire production lines can stall. Manufacturing firms use predictive analytics and succession planning to forecast gaps and prepare internal apprentices or external contractors to fill critical functions.
Public Sector and Municipal Services
Snowplow drivers, transit workers, or sanitation crews cannot be easily replaced. Municipalities that have union-specific contingency plans and mutual-aid agreements with neighboring jurisdictions are better positioned to manage essential services during walkouts.
The Role of Technology in Staffing Contingency Planning
Modern workforce planning has evolved beyond Excel sheets and headcount reports. Today, organizations rely on advanced technologies to make contingency planning more responsive and data-driven.
1. AI-Powered Workforce Analytics
Artificial intelligence can flag patterns in absenteeism, burnout risk, and resignation likelihood—giving staffing leaders early warning of potential disruptions.
2. Real-Time Labor Market Data
Tools like Lightcast or LinkedIn Talent Insights can help anticipate labor availability by region and occupation, enabling proactive sourcing before a crisis hits.
3. Automated Scheduling Platforms
Platforms such as Deputy, UKG, or Shiftboard allow for instant schedule modifications and team communication when emergency changes are needed.
4. Talent Cloud Networks
Platforms like Upwork Enterprise and Fiverr Business help businesses tap into skilled workers across the globe within hours.
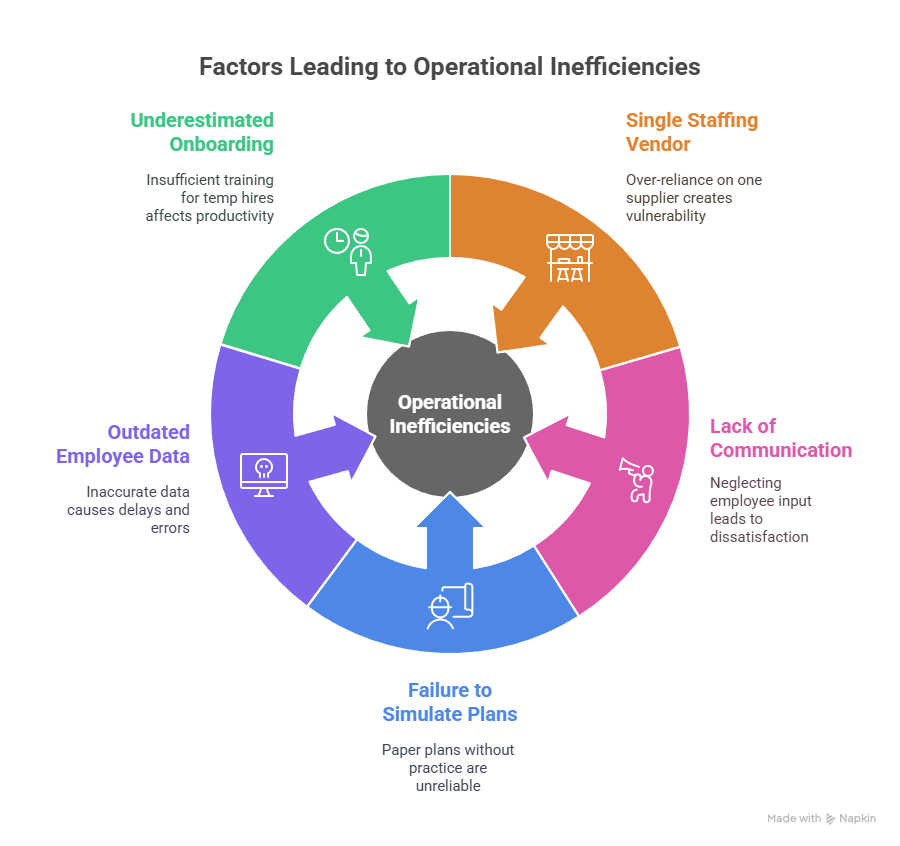
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Staffing Contingency Planning
Even the best-laid plans can fall short if they overlook key components. Here are some common errors to avoid:
- Overreliance on a single staffing vendor: Diversify your supplier base to avoid single points of failure.
- Lack of communication with unions or workforce councils: Neglecting employee input can cause backlash.
- Failure to practice or simulate plans: Paper plans don’t guarantee execution.
- Outdated employee data: Inaccurate databases lead to delays in reassignments.
- Underestimating onboarding timelines for temp hires: Even contract workers need training—build this into your timeline.
Measuring the Success of Your Staffing Contingency Plan
Quantifying the effectiveness of your staffing contingency plan is crucial for ongoing improvement. Consider tracking:
- Response time to disruption
- Downtime avoided
- Temporary labor costs vs. permanent FTE costs
- Employee satisfaction during transition
- Fulfillment rates (e.g., orders shipped, patients treated)
- Attrition among cross-trained employees
Build KPIs into your overall business continuity scorecard.
The Future of Contingency Staffing
As the nature of work continues to evolve—with hybrid models, the gig economy, and automation becoming mainstream—so too must contingency planning strategies. Future-ready staffing teams will prioritize:
- On-demand talent marketplaces
- Automated redeployment tools
- Globalized talent sourcing
- Scenario-based modeling in workforce software
- Employee wellness as a retention buffer
Companies that treat contingency planning as a dynamic, integrated part of their workforce strategy—not just a compliance checkbox—will be better equipped to handle the turbulence of tomorrow’s labor market.
Final Thoughts: Building a Future-Proof Workforce
Contingency planning for staffing has evolved beyond a mere operational consideration; it is now a fundamental pillar of organizational resilience, business continuity, and the pursuit of operational excellence. In today’s dynamic and often unpredictable global landscape, organizations that proactively invest time and resources in comprehensive workforce preparedness will undoubtedly gain a significant competitive advantage. This involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing a thorough assessment of potential vulnerabilities, the deliberate cultivation of robust and diverse talent pipelines, and the strategic adoption of flexible, adaptable technologies. Such an integrated strategy will position businesses to navigate and successfully mitigate labor disruptions, regardless of their origin—be it anticipated internal turnover, unexpected resignations, large-scale external catastrophes like natural disasters, economic downturns, or global health crises.
At its core, effective staffing contingency planning transcends simple problem-solving; it embodies the principle of preparedness. This preparedness is not merely about having a backup plan; it’s about embedding foresight and adaptability into the very fabric of an organization’s talent strategy. In an era increasingly defined by rapid change, unprecedented challenges, and continuous uncertainty, preparedness is no longer a reactive measure but a proactive and indispensable strategic advantage. It empowers organizations to not only survive but to thrive amidst disruption, ensuring continued productivity, employee well-being, and sustained business success.